Intro to Variant Call Format
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 5 minQuestions
How are genotypes and metadata stored in a VCF?
Objectives
Describe the purpose of FORMAT and INFO fields.
Describe what the rows and columns of a VCF represent.
In the setup, you downloaded a compressed VCF file and saved it to
your data directory. Depending on your operating system and what you have
installed, you may be able to preview it from your “Terminal” tab with the
following code. If zless is not available, don’t worry, since everything
else we do will happen in R. To quit zless, type q.
zless data/hmp_agpv4_chr1_subset.vcf.bgz
##fileformat=VCFv4.1
##fileDate=20201110
##HapMapVersion="3.2.1"
##FILTER=All filters passed
##FORMAT=<ID=GT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Genotype">
##FORMAT=<ID=AD,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description="Allelic depths for the reference and alternate alleles in the order listed">
##FORMAT=<ID=GL,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description="Genotype likelihoods for 0/0, 0/1, 1/1, or 0/0, 0/1, 0/2, 1/1, 1/2, 2/2 if 2 alt alleles">
##INFO=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Total Depth">
##INFO=<ID=NZ,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Number of taxa with called genotypes">
##INFO=<ID=AD,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description="Total allelelic depths in order listed starting with REF">
##INFO=<ID=AC,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description="Numbers of ALT alleles in order listed">
##INFO=<ID=AQ,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description="Average phred base quality for alleles in order listed starting with REF">
##INFO=<ID=GN,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description="Number of taxa with genotypes AA,AB,BB or AA,AB,AC,BB,BC,CC if 2 alt alleles">
##INFO=<ID=HT,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Number of heterozygotes">
##INFO=<ID=EF,Number=.,Type=Float,Description="EF=het_frequency/(presence_frequency * minor_allele_frequency), if 2 alt alleles,EF for AB,AC,BC pairsis given; from 916 taxa of HapMap 3.1.1">
##INFO=<ID=PV,Number=.,Type=Float,Description="p-value from segregation test between AB or AB, AC, BC if 2 alt alleles, from 916 taxa of HapMap 3.1.1">
##INFO=<ID=MAF,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Minor allele frequency">
##INFO=<ID=MAF0,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Minor allele frequency from unimputed HapMap 3.2.1 on 1210 taxa">
##INFO=<ID=IBD1,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="only one allele present in IBD contrasts; based on 916 taxa of HapMap3.1.1">
##INFO=<ID=LLD,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="Site in local LD with GBS map (from 916 taxa of HapMap 3.1.1)">
##INFO=<ID=NI5,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="Site with 5bp of a putative indel from 916 taxa of HapMap 3.1.1">
##INFO=<ID=INHMP311,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="Site peresent in HapMap3.1.1">
##INFO=<ID=ImpHomoAccuracy,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Fraction of homozygotes imputed back into homozygotes">
##INFO=<ID=ImpMinorAccuracy,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Fraction of minor allele homozygotes imputed back into minor allelel homozygotes">
##INFO=<ID=DUP,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="Site with heterozygotes frequency > 3%">
##ALT=<ID=DEL,Description=Deletion>
##ALT=<ID=INS,Description=Insertion>
##contig=<ID=1,assembly="1">
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT 2005-4 207 32 5023 680 68139 697 75-14gao 764 78004 78551S 792 83IBI3 8982 9058 98F1 B4 B7 B73 B76 B8 B97 BKN009 BKN011 BKN017 BKN018 BKN027 BKN029 C521 CAUMo17 chang69 chang7daxian1 CML103 CML103-run248 CML411 CN104 Co109 CT109 D1139 D20 D23 D801 D857 D892 dai6 DM07 dupl-478 E588 E601 F7584 F939 FR14 fu8538 H114 H84 HD568 hua160 huangchanga huotanghuang17 Il14H ji63 K22 Ki11 Ky21 LD61 LH1 LH128 LH190 LH202 LH51 LH60 lian87 liao2204 LP1 luyuan133 Lx9801 M3736 MBUB Ms71 mu6 N138 N192 N42 NC268 NC358 ning24 ning45 NS501 Oh40B Pa91 PHG50 PHG83 PHJ31 PHJ75 PHK05 PHM10 PHN11 PHNV9 PHP02 PHR58
PHT77 PHW17 PHW52 PHWG5 qiong51 R1656 RS710 SC24-1 SG17 shangyin110-1 shen142 SS99 SZ3 tai184 TIL01-JD TIL03 TIL09 Timpunia-1 VL056883
VL062784 W117 W238 W344 W499 W668 W968 W9706 wenhuang31413 WIL900 wu312 XF117 y9961 yan38 Yd6 ye107 ye8112 yue39-4 yue89A12-1 zhangjin6
MAIdgiRAPDIAAPEI-12 MAIdgiRAVDIAAPEI-4 MAIdgiRCKDIAAPEI-9 ZEAhwcRAXDIAAPE ZEAxppRALDIAAPEI-9 ZEAxppRAUDIAAPEI-1 ZEAxppRBFDIAAPEI-3 ZEAxppRBMDIAAPEI-6
ZEAxppRCODIAAPEI-9 ZEAxppRDLDIAAPEI-2 ZEAxujRBADIAAPE 282set_A556 282set_A619 282set_A634 282set_A654 282set_A659 282set_A661 282set_A679 282set_B103 282set_CH701-30 282set_CI187-2 282set_CI31A 282set_CI64 282set_CM7 282set_CML14 282set_CML154Q 282set_CML254 282set_CML287 282set_GT112 282set_H99
282set_I29 282set_IDS28 282set_Ki21 282set_KY228 282set_MS153 282set_Mt42 282set_NC222 282set_NC264 282set_NC338 282set_NC346 282set_NC360 282set_NC366 282set_OH7B 282set_Os420 282set_Pa875 282set_Sg1533 282set_T232 282set_T234 282set_Tx601 282set_Tzi25 282set_Tzi8 282set_VA102 282set_Va14 282set_Va26 282set_W117Ht 282set_Wf9 german_Mo17 german_Lo11 german_FF0721H-7 german_F03802 german_EZ5
1 21000162 1-20689192 G T . PASS DP=853;NZ=1203;AD=844,9;AC=14;AQ=34,34;GN=1195,2,6;HT=2;EF=1;PV=0.001;MAF=0.006;MAF0=0.02;IBD1;ImpHomoAccuracy=0.983941605839416;ImpMinorAccuracy=0 GT:AD:GL 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:6,0:0,18,166 0/0::
0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:3,0:0,9,83 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0::
0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:5,0:0,15,139 0/0:21,0:0,63,583 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:5,0:0,15,139 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:3,0:0,9,83 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: ./.:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:4,0:0,12,111
0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:5,0:0,15,139 0/0:4,0:0,12,111 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:6,0:0,18,166 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:3,0:0,9,83 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:3,0:0,9,83 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:4,0:0,12,111 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:4,0:0,12,111 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:9,0:0,27,250 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:6,0:0,18,166 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:5,0:0,15,139 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/1:2,1:19,0,46 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:3,0:0,9,83 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:1,0:0,3,28 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:3,0:0,9,83 0/0:: 0/0:2,0:0,6,55 0/0:: 0/0:: 0/0::
Wow, that’s a lot to look at. What is the information that we have here?
Below is a diagram of the file to make it a bit easier to digest. We have a header, followed by a table of genotypes.
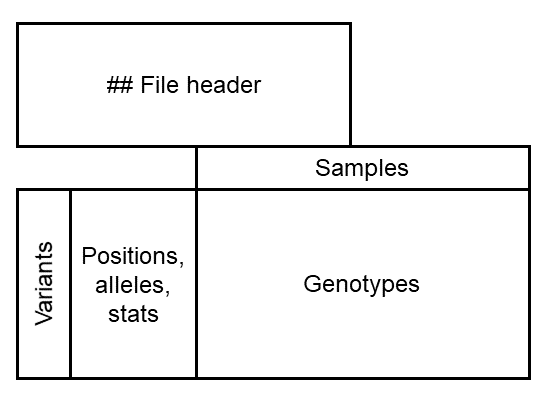
The header
We start with a set of lines beginning with ##. Although these lines aren’t
the most human-readable, if you start looking at the quoted descriptions you’ll
see that the file is “self-documenting”, i.e. there are explanations of what
everything means. We have the date the file was made. The genotype is stored
in a field called GT. DP stores read depth, and MAF stores minor allele
frequency. Many of these are standard fields that are described in the
file format specification.
Others are custom fields, which is why it’s especially helpful to have
descriptions right in the file.
FORMAT fields
We have three fields here tagged as FORMAT: GT, AD, and GL. Anything
with the FORMAT tag indicates information that is stored at the genotype
level, meaning that this is information available for every sample at every
variant.
GT is the genotype. The reference allele is represented by 0, and the
first alternate allele is represented by 1. If there are multiple alleles,
they are represented by numbers 2 and up. (For SNPs, multiple alleles are
rare, but VCF allows any type of variant.) Usually there is a forward slash
between alleles, like 0/0 for a homozygote for the reference allele, or
0/1 for a heterozygote. If genotypes are phased, a pipe is used, so genotypes
might look like 0|0. Polyploid genotypes are allowed, for example 0/0/0/1
for a tetraploid. Missing data are represented by one period for each allele,
for example ./. for diploid data.
AD indicates the sequence read depth for each allele. These are separated by
commas. For example, a homozygous genotype 0/0 might have depths of 5,0
indicating five reads of the reference allele and no reads of the alternative
allele. A heterozygous genotype 0/1 might have depths of 7,4 to indicate
seven reads of the reference allele and four reads of the alternative allele.
Having the read depths allows you to re-do the genotype calling and evaluate
genotype quality yourself.
GL is genotype likelihood (the probability of the observed read depth
distribution, given a genotype), scaled using log10. For a diploid with two
alleles, we’ll see three values, one for 0/0, one for 0/1, and one for
1/1. For example above we see 0,9,83, indicating that 0/0 is very
likely, 0/1 is unlikely but possible, and 1/1 is extremely unlikely. The
reason why there is any uncertainty in the genotype calls is that there could
be sequencing error or undersampling of alleles. There are other fields that
can define this genotype uncertainty including GP, PL, and PP, described in the
file format specification.
These values can be useful for analyses such as GWAS that might want to weight
genotypes by their certainty.
INFO fields
Here we have quite a lot of fields tagged as INFO. The AC field is
described in the file format specification, but all others here are custom.
Each INFO field represents a statistic that was calculated for each variant.
For example, here MAF contains the minor allele frequency. You might use
these fields for filtering markers.
Column headers
After the file header, you should see a row that starts with #CHROM. These
are the column headers for the genotype table. The first nine columns are
always the same:
CHROM: Which chromosome the variant is on.POS: The position (or starting position) of the variant on the chromosome.ID: The name of the variant.REF: The reference allele (the nucleotide matching the reference sequence at this position).ALT: One or more alternative alleles.QUAL: Marker quality. Left as missing (.) by many programs.FILTER: Whether or not the marker passed a filtering step.INFO: Any additional statistics from theINFOfields.FORMAT: WhichFORMATfields are used to code the genotypes, and in what order. This is generally the same for every marker in the dataset, but doesn’t have to be.
After that, there is one column for each sample. In this case the first sample
is called 2005-4. There are no other custom columns, so any custom
information goes into INFO.
Variant rows
Now, the rest of the file is one row per variant. In the first row we see:
- The chromosome is 1.
- The position is 21000162.
- The SNP is named 1-20689192 (after a position in an earlier version of the genome).
- The reference allele is
Gand the alternative allele isT. - No quality score is recorded, and this SNP passed filtering.
- We have a lot of statistics in the
INFOcolumn, separated by semi-colons. - The format is
GT:AD:GL, so that is what we will expect to see for the genotype of each sample. - Under each sample, we see the genotype, allele depths, and genotype likelihoods, separated by colons. Many of these genotypes were imputed and therefore are missing depths and likelihoods.
Once we import this data into R, it will be much more accessible. In the next episode we will cover generally how genomic data and experimental results are stored in BioConductor, which will lead into how we can import and manipulate a VCF.
Discussion
Which FORMAT and INFO fields would you want to use for your analysis, and why? Is there any other information from the VCF that you would use?
Key Points
A VCF is a table with samples in columns and SNPs (or other variants) in rows.
FORMAT fields contain variant-by-sample data pertaining to genotype calls.
INFO fields contain statistics about each variant.